Rotating machinery forms the backbone of modern industries, from power generation to aerospace and manufacturing. To ensure their performance, reliability, and safety, rotor dynamics analysis plays a pivotal role. This specialized field focuses on understanding the vibrational behavior and dynamics of rotors under various operating conditions. This blog explores the need for rotor dynamics analysis, the importance of bearings, the challenges involved, and the types of lateral and torsional analyses critical to maintaining high-performing machinery.

The Need for Rotor Dynamics Analysis
Rotors are subjected to dynamic forces and vibrations due to imbalances, operating loads, and environmental conditions. These factors can cause:
- Excessive Vibrations: Leading to wear, fatigue, and eventual failure of components.
- Resonance at Critical Speeds: Amplifying vibrations and risking catastrophic damage.
- Misalignment and Imbalances: Compromising efficiency and increasing energy consumption.
- System Instability: Resulting from unpredicted interactions between the rotor and supporting structures.
Rotor dynamics analysis is essential to mitigate these risks, enabling engineers to predict vibrational behaviors, optimize designs, and ensure reliable operation. Whether it’s a steam turbine, compressor, or jet engine, rotor dynamics analysis is indispensable for achieving performance and durability.
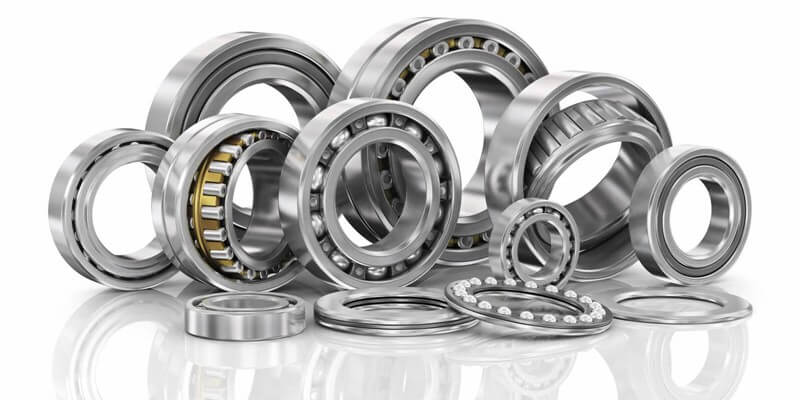
Importance of Bearings in Rotor Dynamics
Bearings are the lifeline of rotor systems, as they provide the necessary support and damping while accommodating rotational motion. Their influence in rotor dynamics cannot be overstated.
- Stiffness and Damping Properties: Bearings define the rotor’s dynamic behavior, affecting critical speeds, vibration amplitudes, and stability.
- Load Distribution: Properly designed bearings ensure balanced load transfer, reducing wear and prolonging rotor life.
- Vibration Mitigation: Bearings with damping properties can absorb vibrational energy, minimizing resonance effects.
- Thermal Considerations: Bearings must handle heat generation from friction without degrading their performance.
The type of bearing (e.g., journal, ball, or magnetic) and its material properties significantly affect the rotor’s overall performance and reliability.
Challenges in Rotor Dynamics Analysis
Despite advancements in computational tools, rotor dynamics analysis remains complex due to:
- Nonlinear Behavior: Nonlinearities in bearings, seals, and material properties make accurate modeling challenging.
- Coupled Dynamics: Interaction between lateral, torsional, and axial dynamics adds complexity.
- Critical Speed Identification: Determining and mitigating resonance points under variable operating conditions requires precision.
- Material and Geometry Constraints: Material anisotropy and intricate geometries of modern rotors demand advanced simulation techniques.
- Thermal and Environmental Effects: Accounting for temperature changes, fluid-structure interactions, and varying operational environments adds layers of complexity.
Engineers must balance these challenges while ensuring timely delivery and cost-effectiveness.
Types of Rotor Dynamics Analysis
Rotor dynamics can be classified broadly into lateral and torsional analyses, each addressing unique aspects of rotor behavior.
Lateral Rotor Dynamics Analysis
This type focuses on transverse vibrations and stability of the rotor.
- Critical Speed Analysis: Identifies speeds at which the rotor’s natural frequencies coincide with excitation frequencies, causing resonance.
- Unbalance Response Analysis: Evaluates vibration amplitudes due to mass imbalances.
- Whirl and Whip Analysis: Studies the interaction between the rotor and fluid forces, which can lead to instability.
- Damping Evaluation: Examines the effectiveness of damping mechanisms in reducing vibrations.
Torsional Rotor Dynamics Analysis
This type addresses angular deformations and stresses caused by torsional vibrations.
- Natural Frequency Calculation: Determines torsional natural frequencies to avoid resonance during operation.
- Transient Torsional Response: Analyzes rotor behavior under sudden changes like startups, shutdowns, or fault conditions.
- Coupled Lateral-Torsional Effects: Investigates interactions between lateral and torsional modes.
- Torque Transmission Efficiency: Ensures safe and efficient power transfer between components.
Both lateral and torsional analyses are essential to design robust and reliable rotating machinery.

Conclusion
Rotor dynamics analysis is fundamental to the success of any rotating machinery. By addressing the challenges and leveraging both lateral and torsional dynamics, engineers can design systems that are efficient, safe, and reliable. Bearings play a crucial role, acting as both enablers and mitigators of dynamic effects. As industries push the boundaries of speed, size, and complexity, the importance of advanced rotor dynamics analysis will continue to grow, ensuring that these machines operate smoothly and sustainably.


Leave a Reply